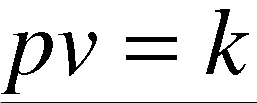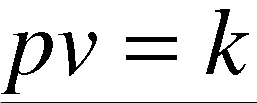Boyle's Law
Boyle's Law, formulated in 1661, is the empirical relation which states that the pressure (p) of a given quantity of gas varies inversely as its volume (v), at constant temperature (k).
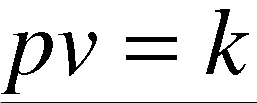
Boyle's Law can be derived from the kinetic theory of gases assuming a perfect (ideal) gas. Real gases obey Boyle's Law at low pressures, pressures less than ten atmospheres. The product pv decreases at high pressures.